Urban transportation is changing. More people are choosing compact electric vehicles like e-scooters and e-bikes for short-distance travel. These machines are quick, lightweight, and easy to store. One important feature often gets overlooked—the bent aluminum frames underneath.
Curved aluminum does more than define a vehicle’s shape. It affects how the frame handles stress, how comfortable it feels to ride, and how well it fits into production lines.
Why Aluminum?
Because City Streets Are Tough
Micromobility vehicles deal with rough surfaces, curb drops, and frequent use. These conditions require frames that are both strong and light.
Aluminum meets both needs. It handles daily impacts while keeping weight low enough for easy carrying. Most riders can lift or store their scooter or e-bike without strain because of the lightweight frame. Aluminum also forms a protective oxide layer, helping it resist corrosion and stay durable in city environments.
Curves That Carry Riders and Design Language
Curved tubes improve more than appearance. They help define how the rider sits, where the components go, and how forces move through the structure.
Frame shape matters, even at city speeds. Curved tubes support better posture, smooth out harsh angles, and distribute vibration across the frame. These features help make short rides more stable and comfortable.
Bending the Backbone: How Frames Are Formed
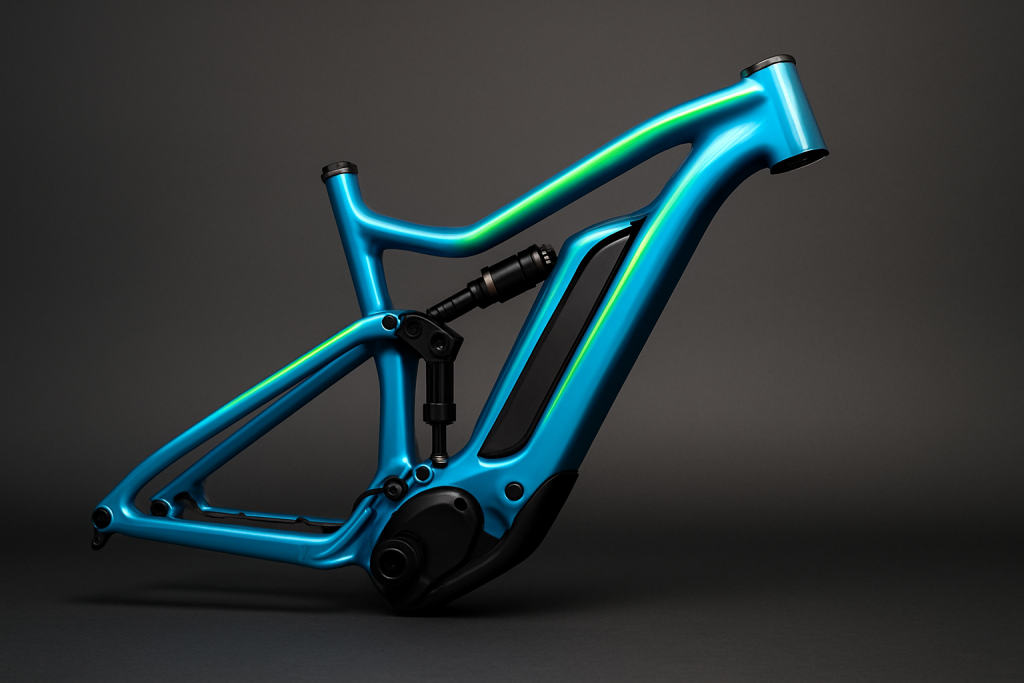

Once engineers finalize the frame layout, they shape the aluminum tubes using bending equipment.
Machines like CNC roll benders and rotary draw benders form accurate curves without damaging the profile. Tight bends can be made while keeping the wall thickness even. This is important when tubes carry loads, route cables, or need to align with welded joints.
These forming processes allow manufacturers to produce accurate shapes that fit directly into assemblies.
Every Bend Has a Purpose
Different parts of a frame use bends for specific reasons:
- Handlebar risers lift the control point to a natural height
- Down tubes and seat stays form the basic structure
- Battery enclosures follow the frame shape for compact integration
- Folding joints and pivot arms let the vehicle collapse for easy storage
- Suspension brackets (on certain models) add comfort over rough roads
Each curved section improves fit, load control, or storage options. Together, they support the ride experience and frame performance.
Manufacturing at Scale: Why Repeatability Matters
In high-volume production, parts need to match exactly so that frames can be built quickly.
Bends must stay within tight tolerances, especially at joints. This accuracy keeps welding and assembly consistent. Fixtures still help hold parts in place, but precise bending means less adjustment during the build. As a result, manufacturers reduce waste and keep production time low.
Greener Cities Start with Smarter Frames
Lightweight frames cut the energy needed to move a vehicle. They also make shipping more manageable during distribution.
Recycled aluminum is common in e-mobility frames. Using it reduces the need for new raw material. Accurate forming helps limit offcuts and scrap, so less material goes to waste. These choices support efforts to reduce the environmental impact of urban transport.
Conclusion
Most people notice the battery or the screen on an e-bike or scooter. But underneath, the frame does the hard work. Its curves, welds, and joints shape how the vehicle rides, how much it weighs, and how long it lasts.
Bent aluminum frames make this possible. Their strength and low weight help support riders while keeping the design compact. These profiles shape how micromobility works in real life and they’ll continue to do so as cities evolve.
Inductaflex forms the curved aluminum profiles that give e-mobility vehicles their shape, strength, and smooth ride.
Looking to shape your next public project? Inductaflex machines handle complex bends with precision and reliability.